Cloud Point of Diesel Fuel
The Problem
The Cloud Point of a diesel fuel is the temperature below which wax forms giving the fuel a cloudy appearance. This parameter is an important property of the fuel since the presence of solidified waxes can clog filters and negatively impact engine performance. The traditional laboratory methods for the measurement of Cloud Point are optical in nature, but rely on cooling the fuel for the wax formation to occur.
The Solution
Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy instrumentation can measure compositional changes in the fuel that will be directly related to the wax formation and hence the Cloud Point. NIR methods can be applied without fuel cooling, in real-time, directly in-process monitoring, or as a laboratory procedure. In either case, NIR is a time and money-saving alternative to traditional methods.
The Background
The NIR region of the electromagnetic spectrum allows the use of the overtone and combination bands of the C-H, O-H, and N-H fundamentals. By measuring the NIR spectra of a series of fuel samples of known Cloud Point, a quantitative model can be developed which will allow the measurement of future samples based only on their NIR spectrum.
The Experimental Set-up
The NIR spectra of a group of different process diesel fuel samples with known (laboratory measured) Cloud Point values were measured between 1100 and 1600 nm using a Guided Wave NIR-O process spectrometer. Figure 1 shows the absorbance spectra of some representative diesel samples collected using an on-line process probe with a 1 cm pathlength.
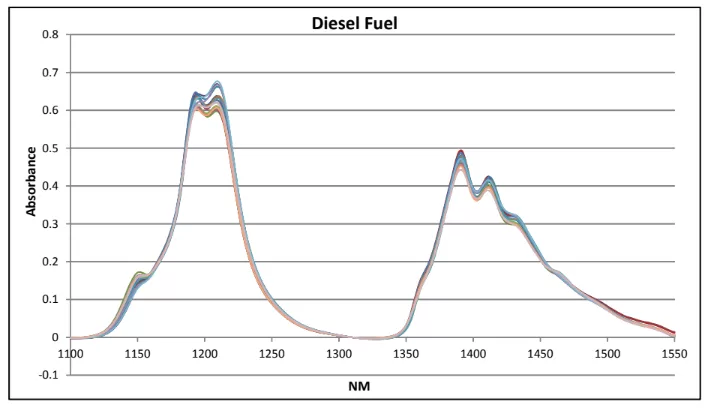
Figure 1: Diesel Fuel NIR Spectra
The Results
Simple pre-processing methods were applied to each data set followed by Partial Least Squares (PLS) Regression analysis. The prediction results from the calibration model are shown in Figure 2. The calibration model produced an RMSEP (root mean square error of prediction) of 1.8 degrees. The RMSEP can be compared with the laboratory reference method error. In this case, the ASTM method reproducibility for Cloud Point ranges from 2.5 to 4 degrees. The NIR method compares favorably with those results.
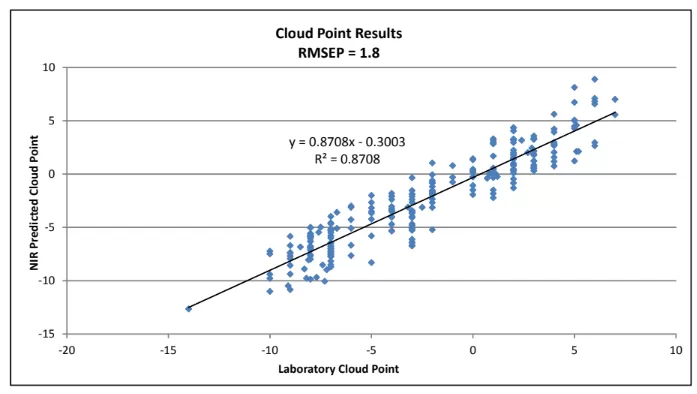
Figure 2: Cloud Point Results
Conclusion
The measurement of the Cloud Point of diesel fuel using NIR spectroscopy is both fast and reliable utilizing the Guided Wave hardware and software tools as described here. This method minimizes the need for laboratory sample collection. Results are available in real-time (seconds) for multiple parameters in complex streams. Guided Wave’s NIR-O™ NIR Process Analyzer system uses fiber optics to allow the NIR-O to be located in a remote (safe) location away from the sample points themselves. It is well suited for measuring many chemical and physical properties of diesel fuel. For more detailed information regarding system specifications please contact a Guided Wave sales or technical specialist.
Questions? We’re here to help.

Support: info@process-insights.com
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR SERVICE
SELLERS AGREEMENT
DATA PROTECTION
FRAUD ALERT
CHINESE
SITE MAP
-
Technology
Products
Blog
Applications
Application Questionnaire
ISO 9001 Certificates
Copyright © 2022 Process Insights, Inc. All Rights Reserved.